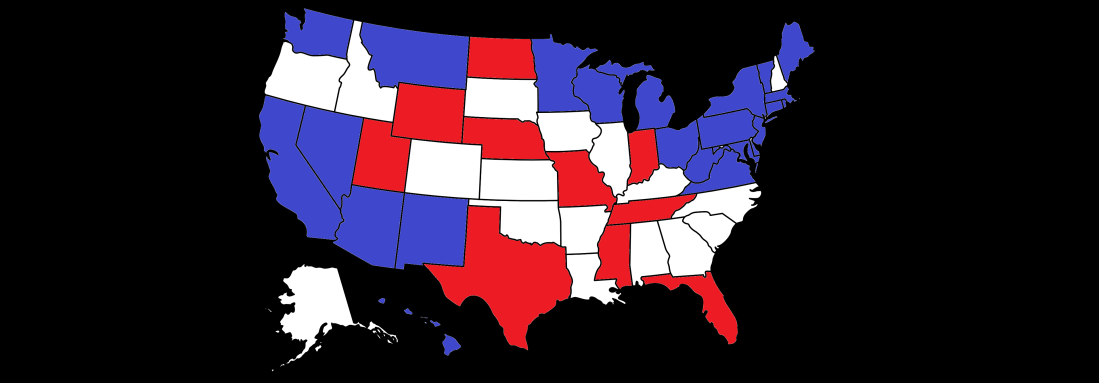
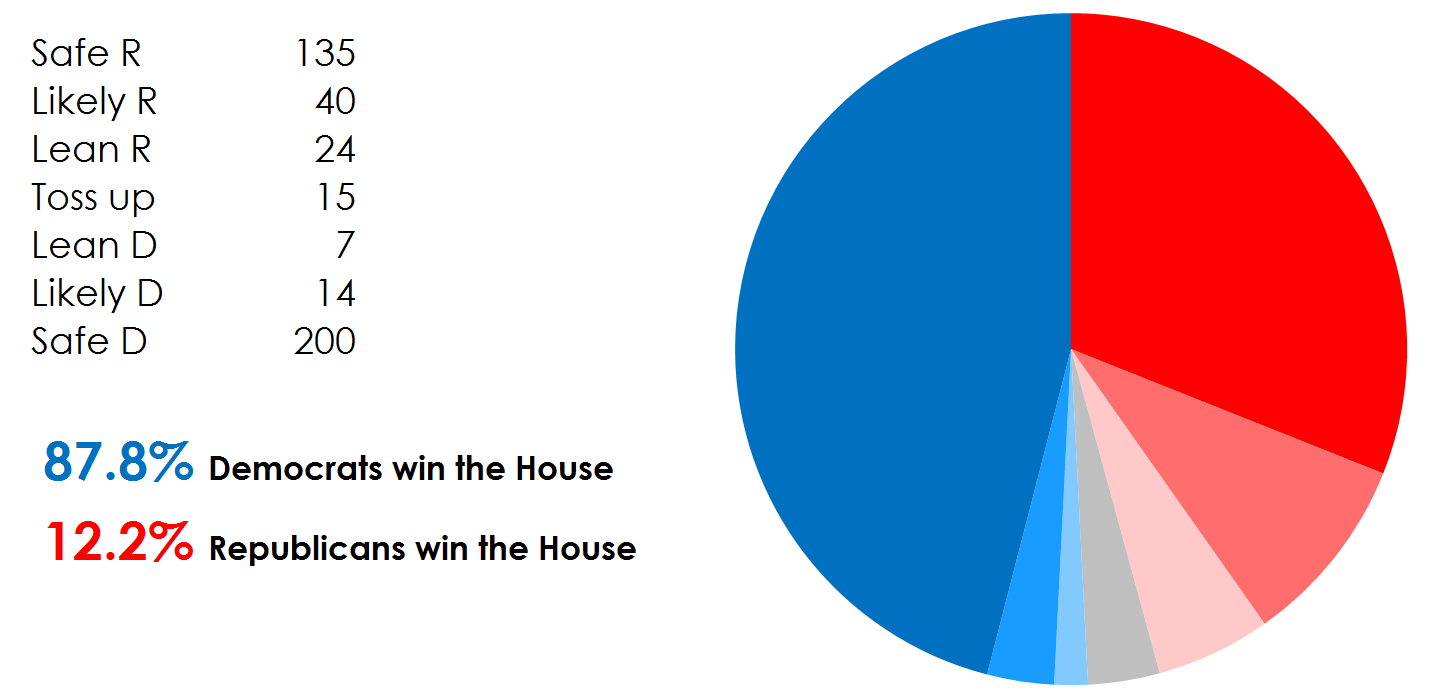
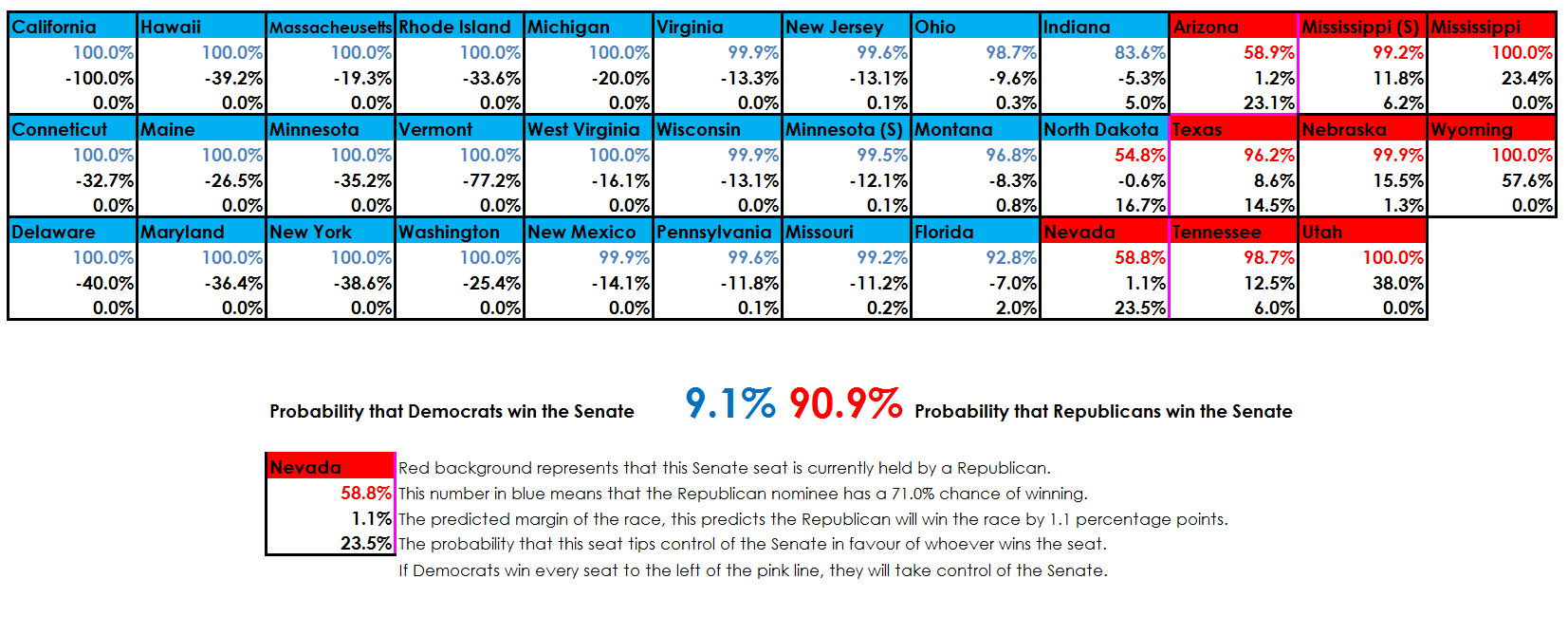
Predictions as of 10/22/2018, as Republicans take a lead in Nevada and Arizona, they look almost sure to hold on to the Senate, while Democrats’ popular vote lead sees them well ahead in the House:
The 2020 Presidential campaign began on Wednesday November 9th 2016, when America woke up to discover Trump’s victory. The race may not officially begin until late 2019, but the battle has already begun, and is sure to intensify the day the midterms are done. Since 2016, the President has made it clear that he intends to run for re-election in 2020, and a rather large number of Democrats have been setting themselves up to challenge him, not to mention several #NeverTrump Republicans. But who actually has a chance of winning?
6. Vice President Joe Biden
On first glance, Joe Biden is a strong candidate for the Presidency. He has the name recognition to cut through a Democratic nomination process that could easily involve 20+ candidates. With 7 terms in the Senate and 2 terms in the Vice-Presidency, no one could ever question his experience. Combine this with his close relation to Obama, who is now seen as practically the father of modern Democratic politics, and he seems a strong contender to win the nomination. Having done so, he could run a campaign on his traditionally moderate politics. He’s always tried to position himself as a man of the people, and his trips to Wisconsin and Michigan clearly indicate some thought about a potential 2020 strategy. Add to this the fact that he was born in Pennsylvania, perhaps the most important swing state in the country at the moment, and he may seem like the perfect answer to Trump.
But Biden has run for the Presidency twice before, in 1988 and 2008, losing horribly both times. 1988 is particularly interesting, as Biden was considered a strong candidate from the very beginning, until he was destroyed by a long string of controversies: Accusations of plagiarizing speeches from the leader of the British Labour Party, as well as Robert F. Kennedy, John F. Kennedy, and Hubert Humphrey; involvement in plagiarism whilst he was at law school; lying about graduating in the top half of his class (he came 76th/85); claiming he earned 3 degrees when in fact he only got 1; and claiming that he received a full scholarship, when in fact he only got a half-scholarship. Biden is also, to be blunt, very old, currently aged 75. This means that by the end of a two term Presidency starting in 2021, he would be 86 years old. On top of the obvious mental and physical health concerns associated with this, it’s worth noting that during the primaries for the midterms, Democrats have tended to prefer younger, female candidates, and anti-establishment candidates have also been doing a little better than expected. Joe Biden is very strong on paper, and has a perfectly good shot, but it seems as though his time has probably come and gone.
5. Senator Kirsten Gillibrand
So how about a young(er), more liberal, female Democrat? Elected once to the House and thrice to the Senate, soon to become four times as she romps to victory in her New York re-election bid, Kirsten Gillibrand may well be the new face of the Democratic Party. With the weight of the mighty New York Democrats behind her, she is a fundraising titan, with $20 million raised towards defending her perfectly safe Senate seat this cycle alone. And though she may be a full blown liberal today, at the beginning of her political career she was a much more moderate Democrat, something she could plausibly call upon once she’s got the nomination in the bag and needs to appeal to the nation as a whole. On the other hand, her ties to the Clinton family and her being a female New York Democrat may well make it very easy for her to become linked in voters’ minds to Hillary Clinton, which would almost certainly not be a good thing for her campaign. Interestingly, unlike some on this list, she hasn’t yet visited Iowa or New Hampshire, the early primary states, which is considered a key step in building up for a Presidential campaign. Even unconventional candidates like Trump visit these states well before the primaries begin, so this might indicate that she isn’t yet sure about running in 2020, hence her place near the bottom of this list.
4. Senator Kamala Harris
Who’s an even more powerful and wealthy ally in a Democratic primary process than the New York Democrats? The California Democrats of course! Kamala Harris is one of a tiny group of candidates who could have a chance at outmatching Gillibrand on fundraising, and is another comparatively young female Senator. She’s even more liberal than Gillibrand, and although she is relatively new to the Senate, this could almost work in her favour, as younger Democrats seem keen to get rid of the old guard of the Party. As if this weren’t enough, she is the best candidate on this list for appealing to the Democrats’ African-American base, which is crucial during primaries. This could also be very useful during a general election. Although many Democrats believe that their path to victory in 2020 is to regain the Upper Midwest, specifically Wisconsin, Michigan, and Pennsylvania, this is hardly their only plausible route. By motivating African-American turnout, Harris could make a serious play for Florida and North Carolina, and perhaps even make Georgia and Arizona genuinely competitive. With the Trump campaign also needing to defend slim and faltering majorities in the Upper Midwest, this strategy could make for a very strong campaign indeed.
3. Senator Bernie Sanders
To all intents and purposes, Bernie Sanders is already running for President. His 2016 campaign never truly ended, and support for him is still strong within the party. He’s visited the early primary states of Iowa, New Hampshire and South Carolina, and even has a book out this year. The real question is not whether he will run, but whether he can win. We can clearly see from the 2016 primaries that he has a lot of support, he won 43% of delegates and only narrowly lost the popular vote to Hillary Clinton. That said, Clinton was not an especially popular candidate among Party members, hardly inspiring the levels of enthusiasm Obama or Sanders generated. So if Sanders couldn’t beat Clinton, could he beat any of the candidates on this list?
Furthermore, at 77 he’s even older than Biden, there has been some talk of a one term pledge, where he promises not to run for re-election, but not from Sanders himself, and it’s likely that such a pledge would harm him during the nomination process as Democrats will be keen to get a strong incumbent into office to secure a win in 2024. In a general election, he may struggle due to being perceived as a socialist, which is still a word with strong negative associations for many Americans, particularly those in high turnout demographics. Despite all this, he is almost definitely running, he has an established base of enthusiastic supporters, and extreme views are growing more popular and electable, as President Trump shows. Sanders is going to be a political heavyweight during the primaries, and his chances should not be underestimated.
2. Senator Elizabeth Warren
Elizabeth Warren is Hillary Clinton’s natural successor, and the one to watch in the Democratic primaries. She has her finger on the pulse of the party, is generally a very skilled politician, and has incredible fundraising abilities with the support of the Massachusetts Democrats, having raised $34 million for her totally uncompetitive re-election campaign this year. She was outspoken on opposing Kavanaugh, has been a fierce Trump critic since the beginning of the 2016 campaign, and was rumoured to be a possible VP pick for Clinton. She has strong support from the left and centre of the Party membership and from across the party establishment – she even received two electoral votes for the Vice Presidency in 2016 from faithless electors. She is running, and she is utterly formidable. A political juggernaut like her on the left wing of the Party may well instantly knock Gillibrand and Sanders out of the running after the first couple of primaries, and if she manages to win the Democratic nomination she would be a similarly fierce candidate against Trump. The only conceivable mark against her is her close association with the deeply unpopular Clinton, which will likely be quietly harming her campaign throughout the process.
1. President Donald Trump
This one is obvious. We know he’s running, we know he’s so popular amongst Republican members that he’s practically guaranteed the nomination, and as an incumbent in an age of two term Presidents we know he has a good shot at winning. His unpopularity is overblown, he’s managing about 42% approval ratings, only slightly worse than Obama’s were at this point in his Presidency. Although the 2018 midterms are looking to be messy for the GOP, holding level in the Senate and losing about 40 House seats, the 2010 midterms were much worse for Obama, with the Democrats losing 6 seats in the Senate and 63 in the House. This all suggests that Trump should be just fine in 2020.
On the other hand, Obama had a lot more room for error between his campaigns. In 2008, he was elected with a 7.2 point popular vote margin and 365 electoral votes, whereas Trump actually lost the popular vote by 2.1 points in 2016 and received only 304 electoral votes. Obama could comfortably afford to lose North Carolina, Indiana, and the 2nd congressional district in Nebraska in 2012 and see his popular vote margin shrink to 3.9 points, while still winning very well. Trump has no such luxuries in 2020. He needs to hold on to very narrow margins in Florida, Michigan, Wisconsin and Pennsylvania, as well as protecting unreliable Republican majorities in North Carolina, Ohio, Iowa and Arizona. He can afford to lose one or two of these, but no more. In terms of opportunities to attack, Trump has New Hampshire, Nevada and perhaps Maine at large. With only 4, 6 and 2 electoral votes respectively, none of these are very exciting for him. However, Minnesota has a full 10 electoral votes, and although it hasn’t voted for a Republican Presidential nominee since 1972, Clinton only won it by 1.5 points in 2020, so Minnesota is very much on the table and could potentially turn the election on its head. Trump is by far and away the most likely candidate to win the Presidency in 2020, despite a variety of strong potential challengers setting themselves up to face him down, and the power of incumbency should not be underestimated.