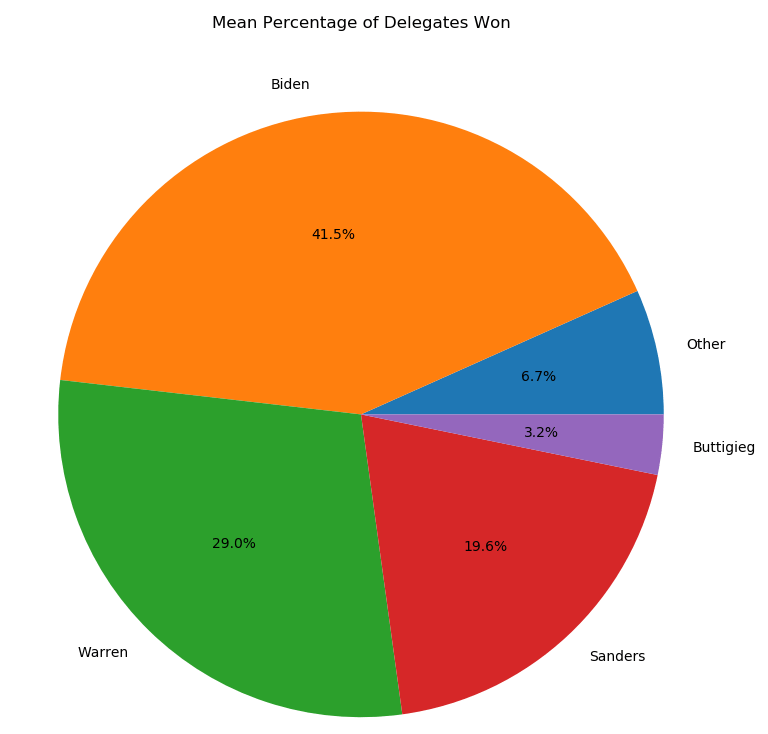
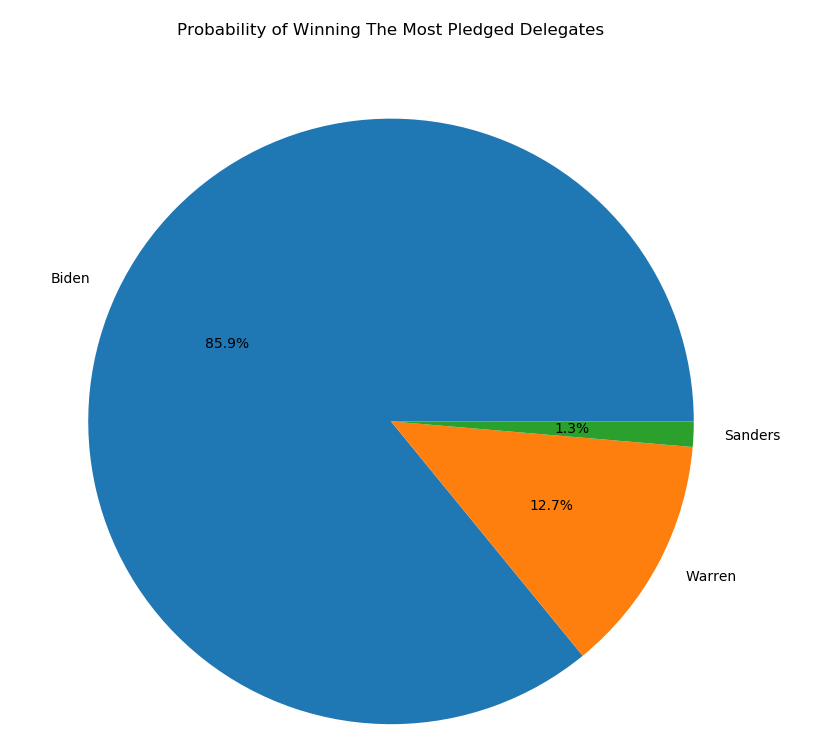
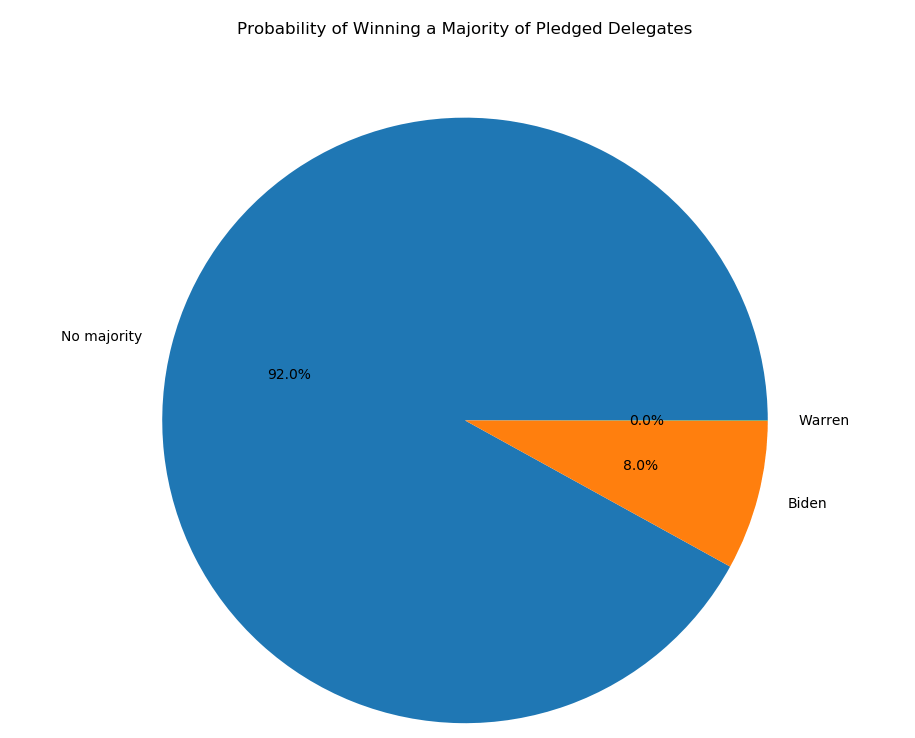
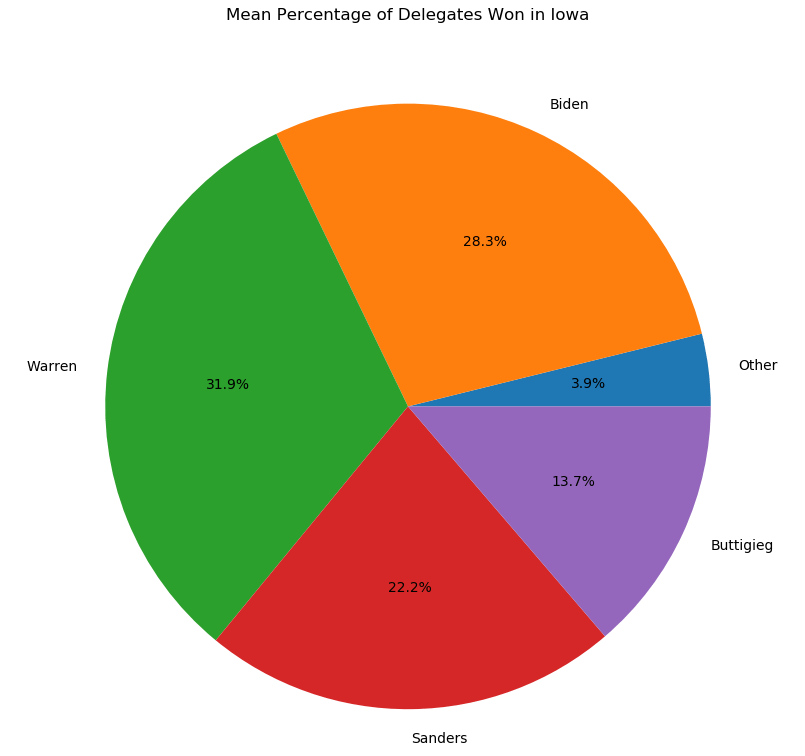
Do you find the Iowa caucus system confusing? Don’t worry, so does the Iowa Democratic Party. It’s the morning after and there are still zero official results. Instead, we have chaos. The Party has failed to provide a thorough or consistent explanation for the absence of results. Reports from Iowa suggest that pretty much everything that could have gone wrong, has.
The key issue seems to be technical problems with an app precincts use to report their results. The technical helpline provided for this app is overloaded, with hold times of more than an hour and some callers being hung up on as soon as they get through to a technician. The backup system for reporting results, based on phone calls, also appears to have collapsed. Additionally there are reports of widespread confusion at caucus sites regarding the process itself, including among some organisers as a result of changes in the system since 2016.
Nevertheless, both the Buttigieg and Sanders campaigns have effectively declared victory, citing anecdotal reports from their own representatives at limited numbers of precincts, and unofficial preliminary results from <2% of precincts from the AP. Meanwhile the Biden campaign is casting aspersions on the legitimacy of the process, perhaps pre-emptively making excuses for what could have been a disappointing night for Biden. The President is also jumping in, insinuating that there exists a conspiracy in Iowa to manipulate the election results. This is one of many misinformation campaigns, with another example being the widespread retweeting of a report of Biden dropping out of the 2008 race, attempting to pass it off as being about 2020.
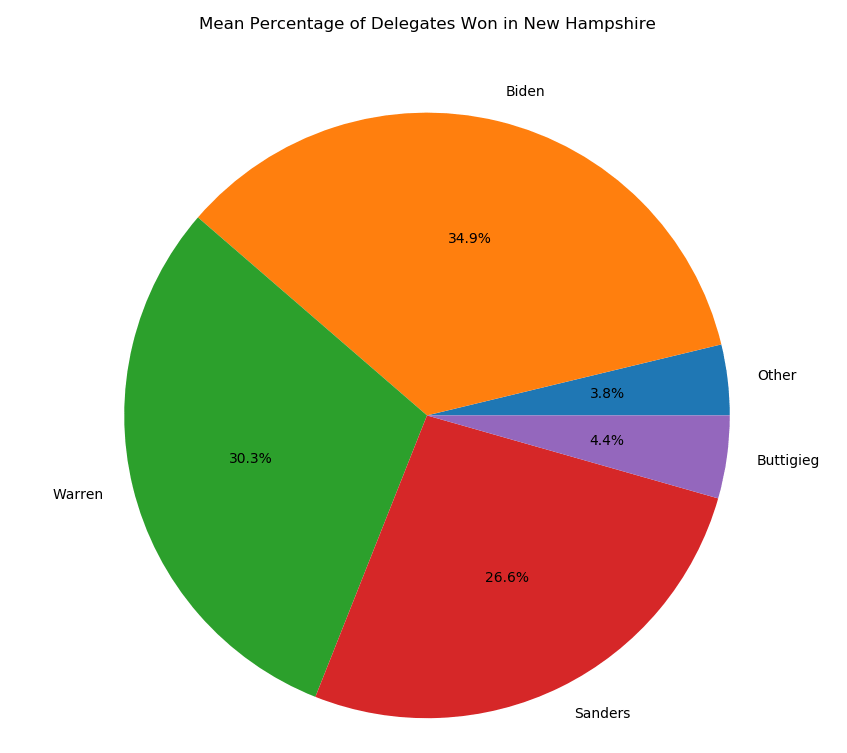
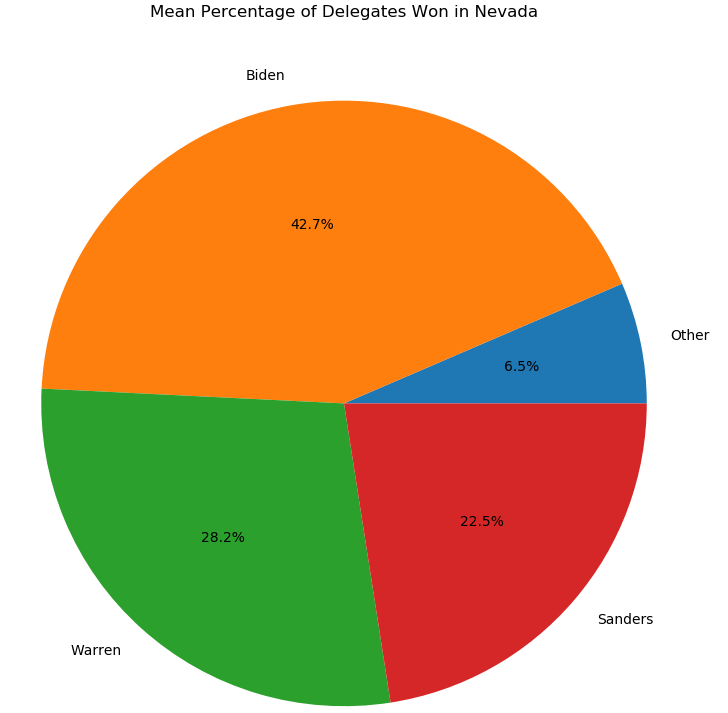
This is a disaster for Iowa, calling into question the caucus system and Iowa’s traditional position as first in the primary calendar. If Iowa were to switch from a caucus to a primary system, it would fall victim to a New Hampshire state law requiring the state to always have the earliest primary. This year, we can expect Iowa’s influence to be significantly decreased due to the confusion and mixed messages. This is probably good news for Biden, who was comparatively weak in Iowa, and disastrous for candidates such as Buttigieg and Klobuchar who built their entire campaigns on winning Iowa. We could now see New Hampshire become the most important state in the primary, and the power of Nevada and South Carolina magnified dramatically. Sanders particularly could stand to benefit due to his strength in New Hampshire, but this is uncharted territory, so the exact impact of tonight’s debacle is unpredictable.
For now, we recommend that you don’t take any of the currently available data seriously. Entrance polls, photos of caucuses, campaigns releasing their own biased estimates, and preliminary results from a tiny proportion of precincts are all very weak data points. We are going to have to wait for the final, official results. Thankfully, there is a paper trail for the caucuses. Therefore, if the worst comes to the worst, the Party can painstakingly recount every vote and eventually arrive at accurate, reliable results. Campaigns have been told that results should be released later today, but at this stage there’s really no telling whether or not that will happen.